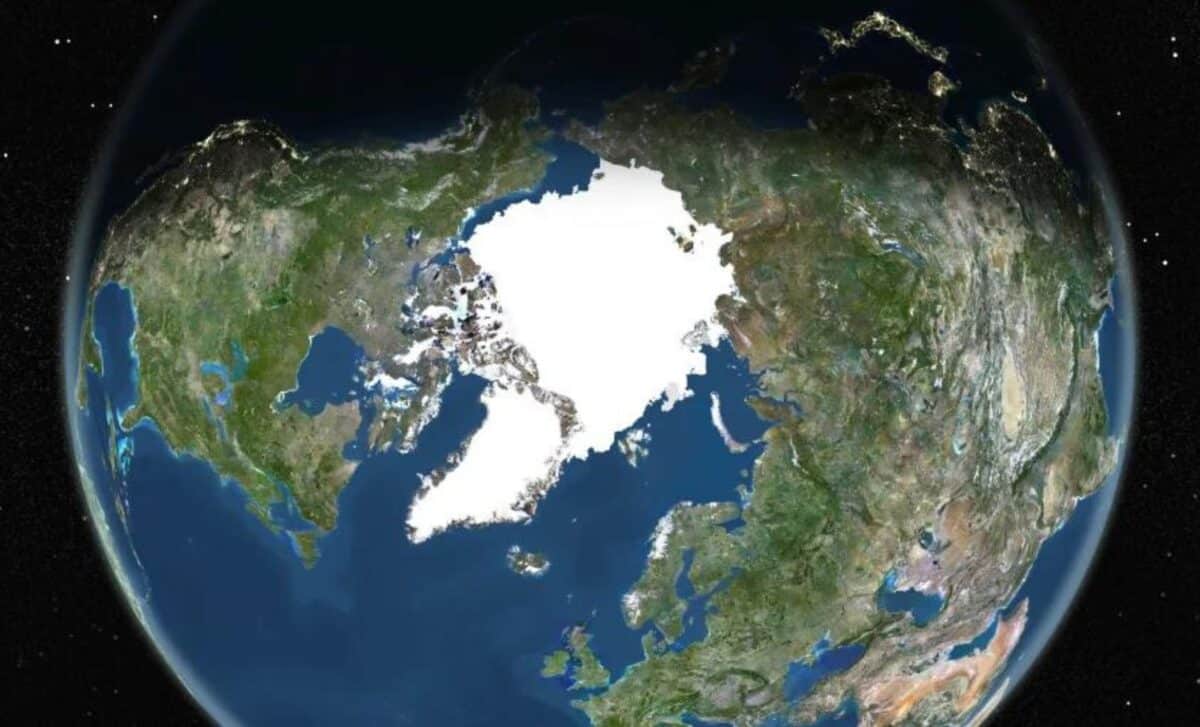
Recent research has revealed that the melting of polar ice caps, driven by climate change, is causing Earth's rotation to slow down, leading to an increase in the length of days.
This phenomenon, explored in studies published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, underscores the profound impact of global warming on our planet's natural processes.
The Impact of Polar Ice Melt on Earth's Rotation
The study highlights that water flowing from Greenland and Antarctica, as a result of melting ice, is adding mass around the equator. This redistribution of mass is similar to a figure skater extending their arms to slow their spin. Benedikt Soja of ETH Zurich explains, “The initially fast rotation becomes slower because the masses move away from the axis of rotation, increasing physical inertia.” This process is causing Earth to spin more slowly, thereby increasing the length of days by a few milliseconds.

For centuries, the primary cause of Earth's rotational slowdown has been the gravitational pull of the Moon, known as tidal friction, which causes a gradual deceleration of about 2.40 milliseconds per century. However, the new study suggests that the effect of climate change on Earth's rotation is becoming more significant. Surendra Adhikari from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory notes, "If humans continue to emit greenhouse gases at a high rate, the effect of a warming climate will be greater than that of the Moon's pull by the end of the 21st century."
Implications for Space Navigation and Technology
The study also explores the broader implications of this slowdown. A slower rotation means that the length of each day increases, which can impact various technologies that rely on precise timekeeping, such as GPS. Adhikari explains, "There are definitely a lot of implications for space and Earth navigation. Knowing the exact orientation of Earth at any given moment is crucial when attempting to communicate with a spaceship, such as the Voyager probes that are now well beyond our Solar System."
Precise timekeeping is vital for GPS and other communication and navigation systems. These systems use atomic clocks, which are based on the frequency of certain atoms, to maintain accuracy. With Earth's rotation slowing down, there will be a need for adjustments in these systems to keep them in sync with the planet's rotation. This may involve adding or subtracting "leap seconds" to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to maintain alignment with Earth's changing rotation speed.
Understanding the Long-term Effects
The research team, which includes international scientists, looked at a 200-year period between 1900 and 2100 to understand how climate change has affected and will continue to affect day length. They found that climate change has caused days to become around 0.8 milliseconds longer since 1900. Under a worst-case scenario of high emissions, climate change alone could extend the length of days by 2.2 milliseconds by 2100.
This increase, although seemingly small, is unprecedented. Benedikt Soja remarked, "In the past, the impact of climate change on time has not been so dramatic, but that could be changing. If the world continues to pump out planet-heating pollution, climate change could become the new dominant factor." This shift emphasizes the urgent need for addressing climate change, as it is altering fundamental aspects of our planet's behavior.
Mostafa Kiani Shahvandi, another study author and geoscientist at ETH Zurich, mentioned that some studies have suggested a correlation between longer days and an increase in earthquakes. However, this connection remains speculative and requires further research to establish any clear link.
The melting of polar ice caps due to climate change is causing Earth to spin more slowly, increasing the length of days. This research highlights the extensive impact of human activities on our planet, affecting not only the environment but also fundamental aspects of timekeeping and technology. As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, understanding its wide-ranging effects remains crucial.