The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT), known for capturing the first image of a black hole, is set to receive significant upgrades that will enhance its capabilities and potentially unlock new mysteries of black holes.
This next-generation EHT will feature additional telescopes and advanced technology, enabling it to observe at multiple frequencies and achieve unprecedented resolution.
Enhanced Capabilities of the Upgraded Event Horizon Telescope
The upgraded EHT will include ten new dishes and incorporate cutting-edge technology to expand its observational capabilities. The new system will observe at 86, 230, and 345 GHz simultaneously, utilizing frequency phase transfer techniques.
This technique allows lower frequency data to supplement higher frequencies, enabling longer integration times and more detailed observations. The EHT's ability to detect the photon ring—a region where light orbits around a black hole—will be significantly improved, allowing astronomers to explore the extreme environments near black holes with greater precision.
The prospect of capturing the photon ring of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A*, and the black hole at the center of M87, is a key focus of this upgraded system.
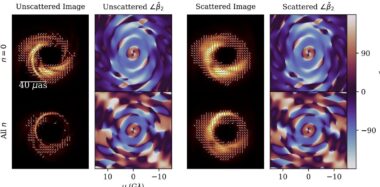
Unraveling the Structure of Magnetically Arrested Disks
The EHT's new capabilities will also enhance our understanding of magnetically arrested accretion disks (MADs), which are present in many supermassive black holes, including those at the centers of M87 and Sagittarius A*.
In these systems, magnetic fields are so strong that they can disrupt the flow of accreting material, leading to the formation of powerful jets. "The studies of the supermassive black hole at the center of M87 and Sagittarius A suggest a magnetically arrested accretion disk," the team noted.
The enhanced sensitivity and resolution of the EHT will allow scientists to study the complex magnetic and plasma processes in these disks in unprecedented detail, providing insights into how these colossal jets are formed and sustained. Understanding these processes is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of black holes and their impact on surrounding environments.

Implications for Black Hole Research and Beyond
The next-generation EHT's improved sensitivity is expected to be more critical than better processing techniques in detecting the photon ring and other subtle features around black holes. "The higher sensitivity of the new EHT will likely be more critical than better processing techniques in the detection of the photon ring," said researchers Kaitlyn M. Shavelle and Daniel C. M. Palumbo.
This advancement will not only provide more detailed images but also help test fundamental theories of physics, such as general relativity, in extreme gravitational environments. The ability to observe these phenomena in different frequencies will also enable the study of various physical processes, including those that might differ based on the environment or the type of black hole.
The findings from these observations will contribute to a broader understanding of the universe, including the role of black holes in galaxy evolution and the mechanisms behind jet formation.
Preparing for Future Discoveries
As the EHT prepares for these upgrades, the global collaboration continues to refine techniques and technologies to maximize the scientific return from these observations. The addition of more telescopes worldwide will enhance the EHT's resolution and sensitivity, making it possible to capture even finer details of black holes and their surroundings.
This expansion will involve international cooperation and coordination, as telescopes from various countries are integrated into the EHT network. The data collected will be invaluable for astronomers and physicists, offering new opportunities to test theories and models of black hole behavior.
The advancements in the EHT are not just about observing black holes but also about pushing the boundaries of our technological capabilities, showcasing the power of international scientific collaboration.




